Question:
A 1350 kg car moving north at a speed of 35.0 m/s collides with a 2300 kg truck that is moving at an angle of 32 degrees north of west at a speed of 23.0 m/s. The car and the truck stick together after the collision. What is the magnitude of their common velocity after the collision?
Answer:
The magnitude of their common velocity after the collision is 24 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Here we have
Sum of total initial momentum = Sum of total final momentum
Initial momentum = m₁·v₁ + m₂·v₂
Where:
m₁ = Mass of car = 1350 kg
v₁ = Initial velocity of car = 35.0 m/s north
m₂ = Mass of truck = 2300 kg
v₂ = Velocity of truck = 23 m/s 32° north of west
Therefore
v₂ north = 23 × sin 32 = 12.2 m/s and
v₂ west = 23 × cos 32 = 19.51 m/s
Sum of intitial momentum
= 1350 × 35 i + 2300× 12.2 i + 2300×19.51 j = 47250 i + 28032.73 i + 44861.744 j
= 75282.73 i + 44861.744 j
Magnitude of the total momentum =
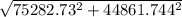
∴ Magnitude of the total momentum = 87635.98 kg·m/s
Total mass after collision = 1350 + 2300 = 3650 kg
Therefore, the magnitude of their common velocity after the collision is given by;
Magnitude of the total momentum ÷ Total mass after collision
= 87635.98 kg·m/s ÷ 3650 kg = 24.009 m/s ≈ 24 m/s.