Answer:
molarity=0.21M
Step-by-step explanation:
First write the balance chemical equation:
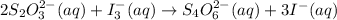
Calculate the oxidation number of each element both side:
Reactant sideoxidaion number:
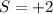
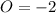
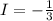
product side oxidation number:
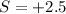
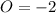
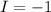
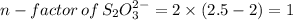
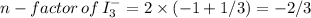 this is change in oxidaion numbe rper atom
this is change in oxidaion numbe rper atom
oxidaion number per molecule=3×(2\3)=2
n-factor of
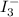 =2
=2
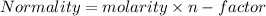 .................................1
.................................1
For thiosulfae solution:
Normality of thiosulfate solution=0.5
lets N1 and N2 are the normality of thiosulfate solution and potassium triiodide solution respectively
lets V1 and V2 are the volume of thiosulfate solution and potassium triiodide solution respectively
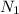 =0.5
=0.5
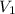 =25ml
=25ml
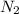 =?
=?
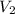 =30ml
=30ml
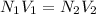
on putting all the value
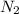 =0.42 normality of potassium triiodide
=0.42 normality of potassium triiodide
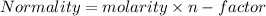
molarity=0.42/2=0.21M
molarity=0.21M