Answer: (a) The value of
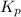 is
is
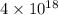 and value of
and value of
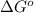 is -106.4 kJ/mol.
is -106.4 kJ/mol.
(b) The value of
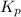 is
is
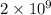 and value of
and value of
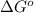 is -53.2 kJ/mol.
is -53.2 kJ/mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) As the given reaction equation is as follows.
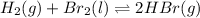
Firs, we will calculate the value of
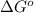 as follows.
as follows.
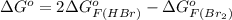
=
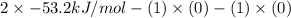
= -106.4 kJ/mol
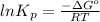
=
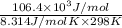
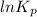 = 42.9
= 42.9
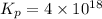
Therefore, the value of
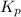 is
is
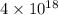 and value of
and value of
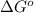 is -106.4 kJ/mol.
is -106.4 kJ/mol.
(b) As the given reaction equation is as follows.
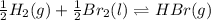
So,
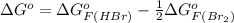
=
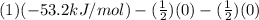
= -53.2 kJ/mol
As,
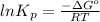
=
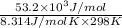
= 21.5
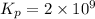
Therefore, the value of
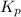 is
is
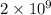 and value of
and value of
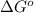 is -53.2 kJ/mol.
is -53.2 kJ/mol.