Answer:
The probability that someone who tests positive actually has the disease is P(S|T)=0.43
Explanation:
A pharmaceutical company has developed a test for a rare disease that is present in 0.5% of the population.
The test is 98% a positive result and the chance of a false positive is 7%
To find the probability that someone who tests positive actually has the disease:
Let S be the event that the rare disease present
P(S)=0.05 and
Let T be the event that the test is positive
P(T)=0.98
Then we have to find the Conditional probability
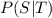 :
:
By using the formula for Conditional Probability is
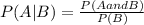
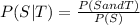
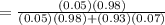
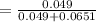
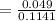
=0.4294
=0.43
∴ P(S|T)=0.43