Answer:
a. 7.89 Ω, 1.14 W
b. By a factor of 2; The batteries would heat up.
Step-by-step explanation:
a. Using Ohm's law, we have that Voltage, V, is directly proportional to Current, I, with the constant of proportionality being Resistance, R. Mathematically:
V = IR
The voltage of the two batteries would be:
V = V1 + V2 = 1.5 + 1.5 = 3.0 V
The current is 380 mA = 0.38 A
Hence, the Resistance, R, will be:
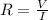
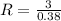
R = 7.89 Ω
Power is given as:
P = IV
P = 3 * 0.38
P = 1.14 W
b. If the batteries are now 4, the new voltage will be:
V = 4 * 1.5
V = 6 V
Power becomes:
P = 0.38 * 6
P = 2.28 W
Comparing with Power in (a) above, we see that the new Power is double the value of the former Power. Hence, the Power has increased by a factor of 2.
It is not advisable to use double the number of batteries to power a flashlight because it would cause the batteries to heat up and thereby, leak or in the worst case scenario, blow up. This could be damaging to the flashlight.