Answer:
0.324 T
Step-by-step explanation:
Parameters given:
Number of turns, N = 1850
Resistance, R = 30Ω
Area of each turn, A =
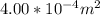
Charge in the circuit, q =
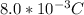
The induced EMF in the coil is given as:
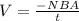
EMF is also given in terms of current, I, and resistance, R, as:
V = IR =
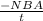
=>
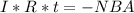
Charge, q, is the product of current and time. Hence:
It = q
=>
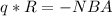
Hence, magnetic field, B, will be:
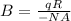
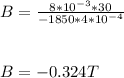
The magnitude of magnetic field, |B| will be |-0.324| = 0.324 T