Answer:
[H₃O⁺] = 2.75x10⁻⁵M
Step-by-step explanation:
The benzoic acid (C₆H₅COOH) dissociates in water producing benzoate ion (C₆H₅COO⁻) and H₃O⁺ ion:
C₆H₅COOH + H₂O ⇄ C₆H₅COO⁻ + H₃O⁺
As pH of the buffer is 4.77, H-H equation gives:
pH = pKa + log₁₀ [Benzoate] / [Benzoic acid]
4.77 = pKa + log₁₀ [0.37M] / [0.10M]
4.20 = pKa
Moles of benzoate and benzoic acid before reaction are:
benzoate: 1.3L × 0.37M = 0.481 moles benzoate
benzoic acid: 1.3L × 0.10M = 0.130 moles benzoic acid
0.056 mol HCl reacts with benzoate ion, producing benzoic acid thus:
C₆H₅COO⁻ + HCl → C₆H₅COOH + Cl⁻
That means, after reaction, moles of benzoate ion and benzoic acid are:
benzoate: 0.481mol - 0.056mol = 0.425 moles benzoate
benzoic acid: 0.130mol + 0.056mol = 0.186 moles benzoic acid
Concentration is:
0.425 moles benzoate / 1.3L = 0.327M
0.186 moles benzoic acid / 1.3L = 0.143M
Replacing in H-H equation, pH after addition of HCl is:
pH = 4.20 + log₁₀ [0.327M] / [0.143M]
pH = 4.56
As pH = -log [H₃O⁺]
[H₃O⁺] =
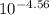 = 2.75x10⁻⁵M
= 2.75x10⁻⁵M