Answer:
![Rate=k[L]^1[M]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/7kyzxs9mk1owwogvq5nfjsa459a6dweqec.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
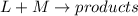
![Rate=k[L]^x[M]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/twcqt9omsesqq1kq7vovc1r703ut2ojtgo.png) (1)
(1)
k= rate constant
x = order with respect to L
y = order with respect to M
n =( x+y)= Total order
a) If [L] is doubled, the reaction rate will increase by a factor of 2:
![2* Rate=k[2L]^x[M]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/4wpfpwcve48hs4bm2qriy93cdp1kyjyevc.png) (2)
(2)
b) If [M] is doubled, the reaction rate will increase by a factor of 4:
![4* Rate=k[L]^x[2M]^y](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/5uji3u5omm5092qdqesgqj1b1qiwut9jil.png) (3)
(3)
Dividing 2 by 1:
![(2* Rate)/(Rate)=(k[2L]^x[M]^y)/(k[L]^x[M]^y)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/wjcc8twd57jbzz47wiex9i69f7a8gvm6yr.png)
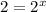
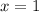
Dividing 3 by 1
![(4* Rate)/(Rate)=(k[L]^x[2M]^y)/(k[L]^x[M]^y)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/6uiy1v8vrnj1htiv0vc40kqya2cajpj91j.png)
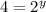
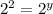
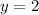
Thus rate law is:
![k[L]^1[M]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/967ra13fg61rikhre9du17xbed6wqweha9.png)