Answer:
Its final temperature is 25.8 °C
Step-by-step explanation:
Calorimetry is the measurement and calculation of the amounts of heat exchanged by a body or a system.
There is a direct proportional relationship between heat and temperature. The constant of proportionality depends on the substance that constitutes the body as on its mass, and is the product of the specific heat by the mass of the body. So, the equation that allows calculating heat exchanges is:
Q = c * m * ΔT
where Q is the heat exchanged by a body of mass m, made up of a specific heat substance c and where ΔT is the temperature variation (ΔT=Tfinal-Tinitial)
When a body transmits heat there is another that receives it. This is the principle of the calorimeter. Then the heat released by the compound will be equal to the heat obtained by the calorimeter.
In this case, you know:
- c= 3.55
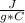
- m=1.20 kg= 1200 g (1 kg=1000 g)
- Tfinal= ?
- Tinitial= 22.5 °C
Replacing:
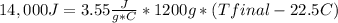
Solving:
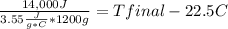
3.3=Tfinal - 22.5 C
3.3 + 22.5=Tfinal
Tfinal= 25.8 °C
Its final temperature is 25.8 °C