Answer:
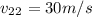
Step-by-step explanation:
In all collisions the total linear momentum of the system is conserved. Therefore:
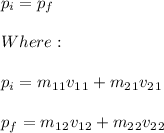
So,
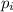 represents the linear momentum before the collision and
represents the linear momentum before the collision and
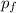 represents the linear momentum after the collision. Now, let:
represents the linear momentum after the collision. Now, let:

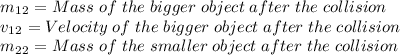
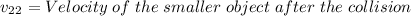
According to the data provided by the problem:
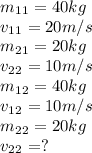
Replacing the data into the linear momentum equation and solving for
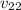 :
:
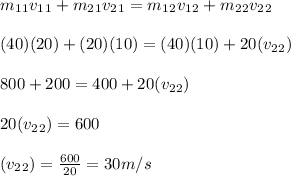
Thus, the velocity of the smaller object after the collision is 30m/s