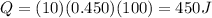1) 385 J
2) 450 J
Step-by-step explanation:
1)
The amount of energy that must be absorbed by a certain substance in order to increase its temperature by
 is given by the equation:
is given by the equation:
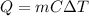
where
m is the mass of the substance
C is its specific heat capacity
 is the increase in temperature of the substance
is the increase in temperature of the substance
For the block of copper in this problem, we have:
m = 10 g is the mass
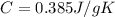 is the specific heat capacity of copper
is the specific heat capacity of copper
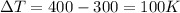 is the change in temperature
is the change in temperature
So, the energy absorbed by the block of copper is
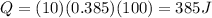
2)
Similarly for the block of iron, the energy absorbed by the iron is given by
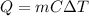
where
m is the mass of the block of iron
C is its specific heat capacity of iron
 is the increase in temperature of the block
is the increase in temperature of the block
Here we have:
m = 10 g is the mass of the block
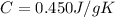 is the specific heat capacity of iron
is the specific heat capacity of iron
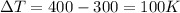 is the change in temperature
is the change in temperature
So, the energy absorbed by the block of iron is