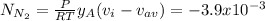Answer:
The molar average velocity is 0.0588 cm/s
The N₂ diffusion velocity relative to the mole average velocity is -0.1428 cm/s
The molar diffusional flux of N₂ is -3.9x10⁻³
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data:
T = temperature = 265 K
O₂ = 25%
N₂ = 60%
CO₂ = 15%
vO₂ = -0.084 cm/s
vN₂ = 0.12 cm/s
vCO₂ = 0.052 cm/s
The molar average velocity is equal:
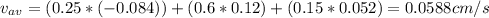
The N₂ diffusion velocity relative to the molar average velocity is:
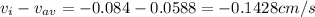
The molar diffusional flux of N₂ is: