Thee given question is incomplete. the complete question is:
The reaction below is carried out at a different temperature at which Kc = 0.055. This time, however, the reaction mixture starts with only the product, [NO] = 0.0100 M, and no reactants. Find the equilibrium concentrations of N2, O2, and NO at equilibrium. The equation is N2(g) + O2(g) <--> 2NO(g)
Answer: Concentration of
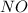 at equilibrium = 0.001 M
at equilibrium = 0.001 M
Concentration of
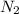 = 0.0045 M
= 0.0045 M
Concentration of
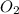 = 0.0045 M
= 0.0045 M
Step-by-step explanation:
Equilibrium constant is the ratio of the concentration of products to the concentration of reactants each term raised to its stoichiometric coefficients.
Initial concentration of
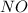 = 0.0100 M
= 0.0100 M
The given balanced equilibrium reaction is,
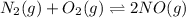
Initial conc. 0 M 0 M 0.0100 M
At eqm. conc. (x) M (x) M (0.0100-2x) M
The expression for equilibrium constant for this reaction will be,
![K_c=([NO]^2)/([N_2][O_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/jnnefylie2oqcfcgpvfa5a7bfh30hfawlb.png)
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get :
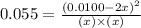
By solving the term 'x', we get :
x = 0.0045
Thus, the concentrations of
 at equilibrium are :
at equilibrium are :
Concentration of
 at equilibrium = (0.0100-2x) M =
at equilibrium = (0.0100-2x) M =
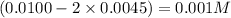
Concentration of
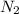 = (x) M = 0.0045 M
= (x) M = 0.0045 M
Concentration of
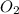 = (x) M = 0.0045 M
= (x) M = 0.0045 M