Answer: Thus value of the equilibrium constant is 1.86
Step-by-step explanation:
Moles of
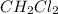 at equilibrium= 0.203 mole
at equilibrium= 0.203 mole
Moles of
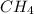 at equilibrium = 0.323 mole
at equilibrium = 0.323 mole
Moles of
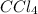 at equilibrium = 0.240mole
at equilibrium = 0.240mole
Volume of solution = 15.2 L
Equilibrium concentration of
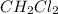 =
=
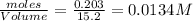
Equilibrium concentration of
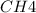 =
=
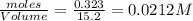
Equilibrium concentration of
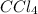 =
=
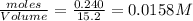
The given balanced equilibrium reaction is,
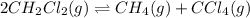
The expression for equilibrium constant for this reaction will be,
![K_c=([CH_4]* [CCl_4])/([CH_2Cl_2]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/79yqe7n6j37gav4nqh3jpn09avxu43ztok.png)
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get :
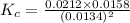

Thus value of the equilibrium constant is 1.86