Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Mean temperature is given by
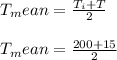
Tmean = (Ti + T∞)/2
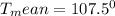
Tmean = 107.5⁰C
Tmean = 107.5 + 273 = 380.5K
Properties of air at mean temperature
v = 24.2689 × 10⁻⁶m²/s
α = 35.024 × 10⁻⁶m²/s
 = 221.6 × 10⁻⁷N.s/m²
= 221.6 × 10⁻⁷N.s/m²
 = 0.0323 W/m.K
= 0.0323 W/m.K
Cp = 1012 J/kg.K
Pr = v/α = 24.2689 × 10⁻⁶/35.024 × 10⁻⁶
= 0.693
Reynold's number, Re
Pv = 4m/πD²
where Re = (Pv * D)/

Substituting for Pv
Re = 4m/(πD
 )
)
= (4 x 0.003)/( π × 6 ×10⁻³ × 221.6 × 10⁻⁷)
= 28728.3
Since Re > 2000, the flow is turbulent
For turbulent flows, Use
Dittus - Doeltr correlation with n = 0.03
Nu = 0.023Re⁰⁸Pr⁰³ = (h₁D)/k
(h₁ × 0.006)/0.0323 = 0.023(28728.3)⁰⁸(0.693)⁰³
(h₁ × 0.006)/0.0323 = 75.962
h₁ = (75.962 × 0.0323)/0.006
h₁ = 408.93 W/m².K