Answer:
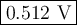
Step-by-step explanation:
We must use the Nernst equation
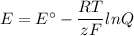
The equation for the cell reaction is is
2Cl⁻(0.384 mol·L⁻¹) + 2Co³⁺(0.324 mol·L⁻¹) ⇌ Cl₂(5.80 atm) + 2Co²⁺(0.158 mol/L)
Data:
E° = 0.483 V
R = 8.314 J·K⁻¹mol⁻¹
T = 25 °C
n = 2
F = 96 485 C/mol
Calculation:
T = 25 + 273.15 = 298.15 K
![Q = \frac{\text{[Cl}^(-)]^(2)[\text{Co}^(3+)]^(2)}{p_{\text{Cl}_(2)}^(2)\text{[Co}^(3+)]^(2)} = (0.384^(2) * 0.324^(2))/(5.80 * 0.158^(2)) =0.1069\\\\E = 0.483 - \left ((8.314 * 298.15 )/(2 * 96485)\right ) \ln(0.1069)\\\\=0.483 -0.01285 * (-2.236) = 0.483 + 0.02872 = \textbf{0.512 V}\\\text{The cell potential is } \large\boxed{\textbf{0.512 V}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/zdy7krqa51lt0ja5a6qahzws1gos5pgzba.png)