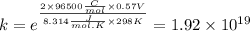Answer:
Value of equilibrium constant is

Step-by-step explanation:
Oxidation:
 ;
;
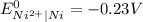
Reduction:
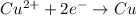 ;
;
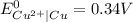
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Overall:
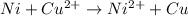
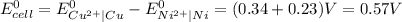
We know,
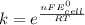
where, k is equilibrium constant, n is no. of electron exchanged, 1F = 96500 C/mol, R is gas constant and T = 298 K
So,