Answer: a. it doubles
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
As the given halide is tertiary halide and the base is strong , it undergoes
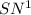 reaction and thus rate depends only on the concentration of tert-butyl bromide.
reaction and thus rate depends only on the concentration of tert-butyl bromide.
![Rate=k[tertbutylbromide]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7ftr3e0c1k91bf04yj1xx9u2zygi4qrwvq.png) [base]^0
[base]^0
k= rate constant
If concentration of both the base and the substrate are doubled ,
![Rate'=k[2* tertbutylbromide]^1[2* base]^0}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/i1ish3dc5m1a1s7fdthqo69n6g1z01x4av.png)
![Rate'=k2^1[tertbutylbromide]^1[base]^0](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/nkojeoepqzbvy46ixiv9fy65ger4rag3c4.png) (2)
(2)
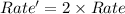
Thus the rate of reaction doubles.