Answer:
Option 2.
Step-by-step explanation:
A turbine produces mechanical work at the expense of fluid energy, that is to say according to the First Law of the Thermodynamics:
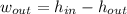
The conditions at inlet and outlet are, respectively:
Inlet - Option 1 (Superheated Steam)
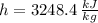
Inlet - Option 2 (Superheated Steam)
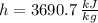
Outlet (Superheated Steam)

The mechanical work per unit mass of each option is determined hereafter:
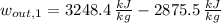
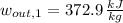
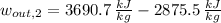
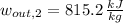
The second option offers more mechanical work per unit mass.