The enthalpy of combustion of 1 mol decane, C10H22, (l), to form CO2 and H2O. ∆Hf0 for decane is —300.9 kJ/mol using the balanced chemical is -6777.9 Kj/mole
Step-by-step explanation:
Balanced chemical equation for combustion of 1 mole of decane:
2
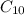
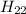 + 31
+ 31
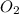 ⇒ 20 C
⇒ 20 C
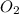 + 22
+ 22
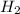 O
O
∆H◦ = −300.9 KJ/mole
enthalpy of combustion of 1 mole decane =?
for 1 mole ∆H◦ = -
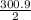
for 1 mole ∆H◦ = - 150.45 KJ
Formula used:
∆H◦reaction of combustion =m. ∆H◦ (products) - n. ∆H◦ (reactants)
m = number of moles of product
n = number of moles of reactant.
from the table it is seen that,
∆H◦ for C
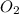 = -393.5 kj/mole
= -393.5 kj/mole
∆H◦ for water = -285.8kj/mole
∆H◦ for oxygen = 0
∆H◦ for decane = -300.9 kj/mole
putting the values in the equation:
∆H◦ = 20(-393.5) + 22(-285.5) = 2(-300.9) +22(0)
= -14151 = -601.8
= -13555.8 kj
The value of enthalpy of reaction or combustion calculated is for 2 moles, hence for 1 mole
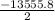
= -6777.9 kJ