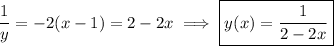4.15
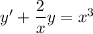
is a linear ODE; multiply both sides by the integrating factor
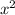 :
:
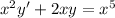
Now the left side can be condensed as the derivative of a product:
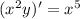
Integrate both sides and solve for
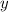 to get
to get
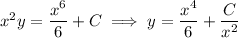
Given that
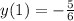 , we find
, we find
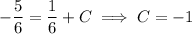
and so the particular solution is
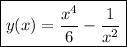
5.15
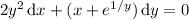
You may be tempted to write this as an ODE in
 , but the ODE in
, but the ODE in
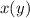 is much easier to solve, since it's linear. Solve for
is much easier to solve, since it's linear. Solve for
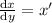 and rearrange the terms:
and rearrange the terms:
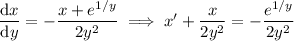
Multiply both sides by the integrating factor
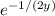 , then solve for
, then solve for
 :
:
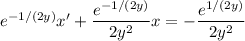
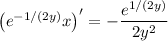
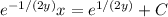
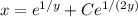
Given that
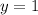 when
when
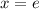 , we have
, we have
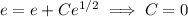
so the particular solution is
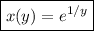
or, by solving for
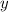 ,
,
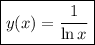
6.15
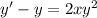
Dividing through both sides by
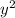 lets us write the equation in Bernoulli form:
lets us write the equation in Bernoulli form:
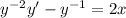
Substitute
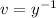 , so that
, so that
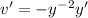 . Then we get an ODE that is linear in
. Then we get an ODE that is linear in
 :
:

Multiply both sides by the integrating factor
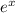 :
:
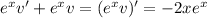
Integrate both sides and solve for
 , then solve for
, then solve for
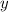 :
:
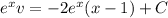
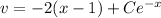
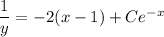
Given that
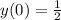 , we find
, we find
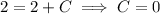
so the particular solution is