Answer:
Molar Concentration =
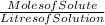
=
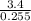
= 13.33
No. of H+ ions present = 13.33
pH value = - log[13.33]
= -1.12
Step-by-step explanation:
The equivalence point, or stoichiometric point, of a substance response is the point at which synthetically identical amounts of reactants have been blended. As such, the moles of corrosive are equal to the moles of base, as per the condition (this doesn't really infer a 1:1 molar proportion of acid:base, simply that the proportion is equivalent to in the condition). It tends to be found by methods for a marker, for instance phenolphthalein or methyl orange. The endpoint (identified with, however not equivalent to the equivalence point) alludes to the point at which the marker changes shading in a colorimetric titration.