Step-by-step explanation:
Starting moles of ethanol acid = 0.020 mol
At the equilibrium 50 % of the ethanol acid molecules reacted
∴ Moles of ethanol acid reacted = 0.020 mol * 50 %/100 %
= 0.010 mol
Moles of ethanol acid remain = 0.020 mol + 0.010 mol = 0.010 mol
Moles of the product
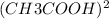 gas formed are calculated as
gas formed are calculated as
0.010 mol CH3COOH * 1 mol
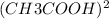 / 2 mol CH3COOH
/ 2 mol CH3COOH
= 0.005 mol
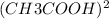
Therefore at the equilibrium total moles of gas present in the vessel are 0.010 mol CH3COOH and 0.005 mol
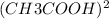
That is total gas moles at equilibrium = 0.010 mol + 0.005 mol = 0.015 mol
Now Calculate the pressure :
0.020 mol gas has pressure of 0.74 atm therefore at the same condition what will be the pressure exerted by 0.015 mol gas
P1/n1 = P2/n2
P2 = P1*n2 / n1
= 0.74 atm * 0.015 mol / 0.020 mol
= 0.555 atm