Answer:
The magnitude of the force is 9.7*10^-8N and has is directed at -11.37°.
Step-by-step explanation:
From the principle of superposition, the electric force on 6.0nC charge is equal to the sum of forces due to 2.0nC charge and 3.0nC charge.
The force due to 3.0nC charge is
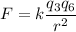
From Pythagorean theorem find find that the distance between the charges is
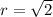 ; therefore,
; therefore,
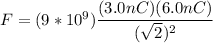
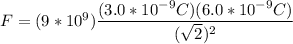
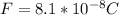 ,
,
which can be broken up into two vector components:
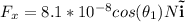
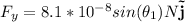
and since
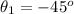 (the angle between the force and the horizontal)
(the angle between the force and the horizontal)


Similarly, for 2.0nC charge since the distance is
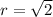
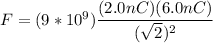
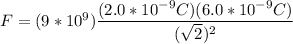
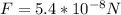 .
.
Since
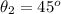 , the vector components are
, the vector components are
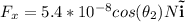
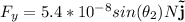
which become


Now, with all the forces in hand it is just a matter of adding them up to find the net force:
In the x- direction
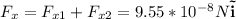
In the y-direction
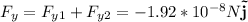
the magnitude of this force is
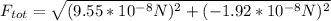
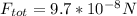
and it is directed at an angle of
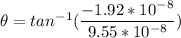
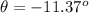 .
.
Hence, the magnitude of the force is 9.7*10^-8N and has is directed at -11.37°.