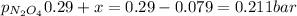Answer:
The partial pressure of NO₂ is 0.958 bar and the partial pressure of N₂O₄ is 0.211 bar
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction is:
2NO₂ = N₂O₄
The equilibrium constant is:
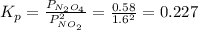
When the volume is double, the pressure will be halved, and will be:
PNO₂ = 0.8 bar
PN₂O₄ = 0.29 bar
The ICE table for this exercise is:
2NO₂ = N₂O₄
I......... 0.8..........0.29
C....... -2x.......... +x
E-----0.8-2x....... 0.29+x
The equilibrium constant is:
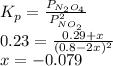
The partial pressure of NO₂ is:
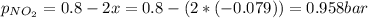
The partial pressure of N₂O₄ is: