The question is incomplete, here is the complete question:
At 25°C, Kp = 2.9 × 10⁻³ for the reaction:
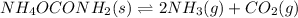
In an experiment carried out at this temperature, a certain amount of NH₄OCONH₂ is placed in an evacuated rigid container and allowed to come to equilibrium. Calculate the total pressure in the container at equilibrium.
Answer: The total pressure in the container at equilibrium is 0.2694 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
Let the initial concentration of
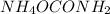 be 'x'
be 'x'
The given chemical equation follows:
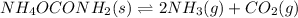
Initial: x
At eqllm: x-y 2y y
The expression of
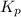 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
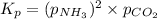
The partial pressure of pure solids and liquids are taken as 1 in equilibrium constant expression. So, the partial pressure of
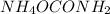 is not seen in the expression.
is not seen in the expression.
We are given:
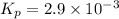
Putting values in above expression, we get:
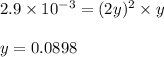
So, the equilibrium partial pressure of ammonia = 2y = (2 × 0.0898) = 0.1796 atm
The equilibrium partial pressure of carbon dioxide = y = 0.0898 atm
Total pressure inside the container at equilibrium =
![p_(NH_3)+p_(CO_2)=[0.1796+0.0898]=0.2694atm](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ddbevq7i3bdnttjyr0wccsw8pmwjqxbdrf.png)
Hence, the total pressure in the container at equilibrium is 0.2694 atm