Answer:
1.144 A
Step-by-step explanation:
given that;
the length of the wire = 2.0 mm
the diameter of the wire = 1.0 mm
the variable resistivity R =
![\rho (x) =(2.5*10^(-6))[1+((x)/(1.0 \ m))^2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/lcdcf6918hjk3qapkvpbfju48j7rfjnox9.png)
Voltage of the battery = 17.0 v
Now; the resistivity of the variable (dR) can be expressed as =
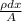
![dR = ((2.5*10^(-6))[1+((x)/(1.0))^2])/((\pi)/(4)(10^(-3))^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/4ezu6qyfnhudnopb609itd72tutimao3xy.png)
Taking the integral of both sides;we have:
![\int\limits^R_0 dR = \int\limits^2_0 3.185 \ [1+x^2] \ dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/jxvw3k3xwsmt4ajaxrc0pfaw5fwh1rzqzi.png)
![R = 3.185 [x + \frac {x^3}{3}}]^2__0](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/ac1mj8ndgqb0wy2cgfosz02awkzp96d5vn.png)
![R = 3.185 [2 + \frac {2^3}{3}}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/l3bsbhz2411mccqby4n60vdo6zt3n3wiev.png)
R = 14.863 Ω
Since V = IR
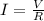
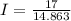
I = 1.144 A
∴ the current if this wire if it is connected to the terminals of a 17.0V battery = 1.144 A