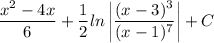If the integral is simply
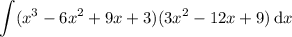
then notice that
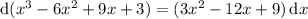
which means you can compute the integral easily with a substitution
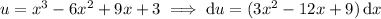
Under this transformation, the integral is
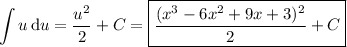
On the other hand, in case you're missing a symbol and the integral is actually
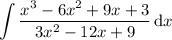
then first carry out the division:
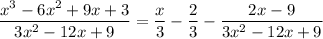
Now,
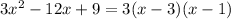 , so to integrate the remainder term you can decompose it into partial fractions:
, so to integrate the remainder term you can decompose it into partial fractions:
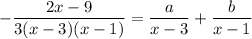

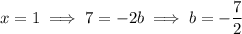
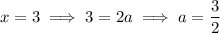
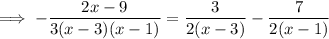
Then the integral would be
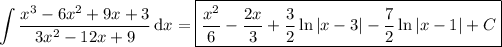
which can be rewritten in several ways, such as