Answer:
ΔH° (Enthalpy change) for the reaction is equal to (-151.5 KJ)
Step-by-step explanation:
Determine the enthalpy for the reaction
COCl₂ (g) + H₂O(l) --> CH₂Cl₂(l) + O₂(g)
It becomes easier to find the unknown value of enthalpy of a particular reaction by applying the Hess's law on the given reaction with the known value of standard enthalpy change.
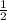 H₂(g) +
H₂(g) +
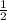 Cl₂(g) --> HCl(g) ΔH=-46 kJ -----------------------------(1)
Cl₂(g) --> HCl(g) ΔH=-46 kJ -----------------------------(1)
H₂O(g) + Cl₂(g) --> 2 HCl(g) +
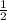 O₂ (g) ΔH=-21 KJ-------------------(2)
O₂ (g) ΔH=-21 KJ-------------------(2)
CH₂Cl₂(l) + H₂(g) +
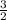 O₂(g) --> COCl₂(g) + 2 H₂O(l) ΔH = 80.5 kJ ----------(3)
O₂(g) --> COCl₂(g) + 2 H₂O(l) ΔH = 80.5 kJ ----------(3)
Equation (1) Multiply by factor 2 we get
H₂(g) + Cl₂(g) ---> 2 HCl (g) ΔH = - 46 x 2 = - 92 KJ ------------(4)
Revers the equation (2) and (3) we get
2 HCl(g) +
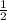 O₂ (g) --> H₂O(g) + Cl₂(g) ΔH=+21 KJ ----------------(5)
O₂ (g) --> H₂O(g) + Cl₂(g) ΔH=+21 KJ ----------------(5)
COCl₂(g) + 2 H₂O(l) --> CH₂Cl₂(l) + H₂(g) +
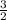 O₂(g) ΔH = - 80.5 kJ -----------(6)
O₂(g) ΔH = - 80.5 kJ -----------(6)
Now add these three equations i.e., (4) + (5) + (6)
we can get these equation
COCl₂ (g) + H₂O(l) --> CH₂Cl₂(l) + O₂(g)
The enthalpy change during the reaction = -92 + 21 -80.5 = - 151.5 KJ