Answer:
About 4.63.
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction between ethanoic acid (CH₃COOH) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) can be described by the following net ionic equation:

40.0 mL of 0.040 M NaOH contains:
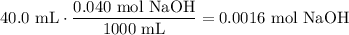
Because NaOH is a strong base, it dissociates completely. Hence, the amount of OH⁻ present is 0.0016 mol. Na⁺ acts as a spectator ion.
50.0 mL of 0.075 M CH₃COOH contains:
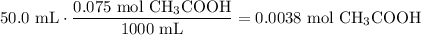
OH⁻ is the limiting reagent of the reaction. Therefore, as the reaction proceeds to completion:
- The amount of OH⁻ drops to 0 mol.
- The amount of CH₃COOH decreases to (0.0038 - 0.0016) mol = 0.0022 mol.
- And the amount of CH₃COO⁻ increases to (0 + 0.0016) mol = 0.0016 mol.
Note that all species present are in a one-to-one ratio.
To find pH, we can use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
![\displaystyle \text{pH} = \text{p}K_a + \log\frac{[\text{Base}]}{[\text{Acid}]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/npkzmquyrpkozr5msys7g13zmbvywquc1t.png)
The total volume of the solution is 40.0 mL + 50.0 mL = 90.0 mL.
Hence, find [CH₃COOH]:
![\displaystyle \left[\text{CH$_3$COOH}\right] = \frac{0.0022\text{ mol}}{90.0\text{ mL}} \cdot \frac{1000\text{ mL}}{1\text{ L}} = 0.024\text{ L}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/55piswqdnefdaqmx581oed992q07fzq8y1.png)
Find [CH₃COO⁻]:
![\displaystyle \left[\text{CH$_3$COO}^-\right] = \frac{0.0016\text{ mol}}{90.0\text{ mL}}\cdot \frac{1000\text{ mL}}{1\text{ L}} = 0.018\text{ M}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/k54vyp7a4hoy15v6z2zf3b0yaxx8d8d8to.png)
Therefore, the pH of the resulting solution is:
![\displaystyle \begin{aligned}\text{pH} & = \text{p}K_a + \log\frac{[\text{Base}]}{[\text{Acid}]} \\ \\ & = (4.75) + \log ((0.018))/((0.024)) \\ \\ & = 4.75 + (-0.12) \\ \\ & = 4.63\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/arswt3jxstjfar0pj55ztdk3rfvq201ps0.png)
In conclusion, the pH of the resulting solution is about 4.63.