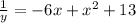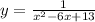Answer:
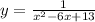
Explanation:
We have given,
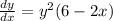
and initial condition
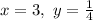
Now,
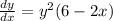
Rearranging the variables, we get
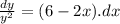
Applying integration both sides, we get
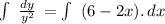
⇒
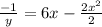
⇒
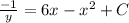
Putting the initial condition (i.e.,
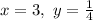 ), we get
), we get
⇒
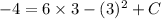
⇒
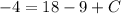
∴
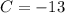
We have,
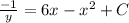
now putting the value of
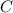 in above equation, we get
in above equation, we get
⇒
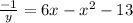
⇒