Answer:
Two statements are true:
- II. The reaction is exothermic.
- III. The enthalpy term would be different if the water formed was gaseous.
Step-by-step explanation:
- C₂H₅OH(ℓ) + 3O₂(g) → 2CO₂(g) + 3H₂O(ℓ); ∆H = –1.37 × 10³ kJ
1. ∆H = –1.37 × 10³ kJ it telling that the enthalpy of the reaction is negative.
That means that reaction releases heat, which, by definition, means that the reaction is exothermic.
Then statement I is false and statement II is true.
2. The enthalpy of a reaction is equal to the enthalpy of the products less the enthalpy of the reactants:
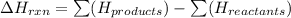
The enthalpy of each substance depends on its state, thus the enthalpy term for water will be different if it is formed as a gas than if it is formed a liquid.
Hence, the enthalpy of the reaction will be different in case the water formed was gaseous, and the third statement is also true.