Answer:
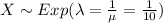
The probability density function would be given by:
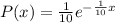
And for this case we want to find this probability:
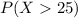
And we can find this probability with the complement rule and the following integral:
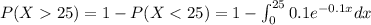
And after solve the integral we got:
![P(X>25)= 1- [-e^(-0.1 x)] \Big|_0^(25) = 1+ [e^(-0.1x) \Big|_0^(25)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/yztr3a1ojqtb0a19xmd7af4jjg6p2b8x0i.png)
And using the fundamental theorem of calculus we got:
![P(X>25) =1 +[e^(-0.1*25) -e^(-0.1*0)]=0.0821](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/n2o89fn1ochtjytwmvjc2gapmf1jgbe9lb.png)
Explanation:
Previous concepts
The exponential distribution is "the probability distribution of the time between events in a Poisson process (a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate). It is a particular case of the gamma distribution". The probability density function is given by:
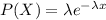
Solution to the problem
For this case we define the random variable X time between arrivals and we know that the distribution is given by:
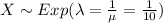
The probability density function would be given by:
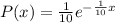
And for this case we want to find this probability:
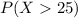
And we can find this probability with the complement rule and the following integral:
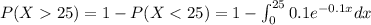
And after solve the integral we got:
![P(X>25)= 1- [-e^(-0.1 x)] \Big|_0^(25) = 1+ [e^(-0.1x) \Big|_0^(25)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/yztr3a1ojqtb0a19xmd7af4jjg6p2b8x0i.png)
And using the fundamental theorem of calculus we got:
![P(X>25) =1 +[e^(-0.1*25) -e^(-0.1*0)]=0.0821](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/n2o89fn1ochtjytwmvjc2gapmf1jgbe9lb.png)