Answer:
![rate=k[UO_2^+]^2[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/lwqtg9lhjlrhimf9n71w5dyj15f9dkb7x1.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
The balanced chemical reaction is:
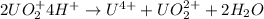
![rate=k[UO_2^+]^n[H^+]^m](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/avbacap9lot17i9st4tj3szrxbdfx6kwqi.png)
where k = rate constant
n = order with respect to
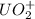 = 2
= 2
m = order with respect to
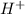 = ?
= ?
n+ m = 3
2+ m = 3
m = 1
Thus m = order with respect to
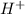 = 1
= 1
![rate=k[UO_2^+]^2[H^+]^1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/rmtm113571s96ew9a882k1psahrcl11im9.png)