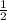Answer:
a
The output power is
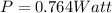
b
The Amplitude would decrease by
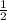
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The diameter of the steel wire is = 1.0mm
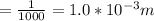
The raduis of this steel wire is
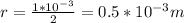
Now from the question we can deduce that the power output is equal to the power being transmitted by wave on the wire this is mathematically represented as
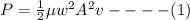
Where
 is the mass per unit length of the wire
is the mass per unit length of the wire
This is mathematically evaluated as
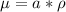
Where a is the area of the the wire =
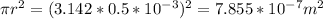
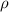 is the density of steel with a generally value of
is the density of steel with a generally value of
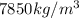
So
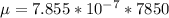
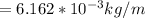
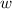 is velocity of the wave
is velocity of the wave
This is mathematically evaluated as
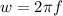
substituting 60Hz for f
We have
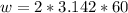
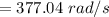
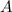 is the amplitude with a given value of 0.50 cm
is the amplitude with a given value of 0.50 cm
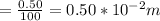
v is the linear velocity of the wave
This is mathematically evaluated as
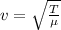
Where T is the tension with a given value of
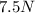
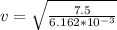
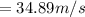
Substituting values into equation 1
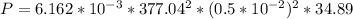
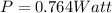
Since the doubling of the frequency does not affect the amplitude and from equation one the output power is
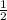 of the Amplitude, Then the Amplitude would decrease by
of the Amplitude, Then the Amplitude would decrease by