Answer:
Option D
The star is at a distance of 100 parsecs.
Step-by-step explanation:
The distance can be determined by means of the distance modulus:
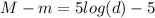 (1)
(1)
Where M is the absolute magnitude, m is the apparent magnitude and d is the distance in units of parsec.
Therefore, d can be isolated from equation 1
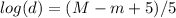
Then, Applying logarithmic properties it is gotten:
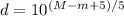 (2)
(2)
The absolute magnitude is the intrinsic brightness of a star, while the apparent magnitude is the apparent brightness that a star will appear to have as is seen from the Earth.
Since both have the same spectral type is absolute magnitude will be the same.
Finally, equation 2 can be used:
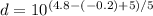
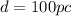
Hence, the star is at a distance of 100 parsecs.
Key term:
Parsec: Parallax of arc seconds