Answer:
Yes, we can conclude that the number of calls per salesperson per week is more than 42.
Explanation:
We are given that a college textbook publishing company, claims that the sales representatives make an average of 42 sales calls per week on professors. To investigate, a random sample of 40 sales representatives reveals that the mean number of calls made last week was 44. The standard deviation of the sample is 1.9 calls.
We have to conduct a hypothesis test to conclude that the mean number of calls per salesperson per week is more than 42 or not.
Let
 = mean number of calls per salesperson per week
= mean number of calls per salesperson per week
SO, Null Hypothesis,
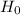 :
:
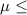 42 {means that the mean number of calls per salesperson per week is less than or equal to 42}
42 {means that the mean number of calls per salesperson per week is less than or equal to 42}
Alternate Hypothesis,
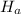 :
:
 > 42 {means that the mean number of calls per salesperson per week is more than 42}
> 42 {means that the mean number of calls per salesperson per week is more than 42}
The test statistics that will be used here is One-sample t test statistics as we don't know about the population standard deviation;
T.S. =
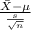 ~
~
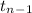
where,
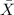 = sample mean number of calls made last week = 44
= sample mean number of calls made last week = 44
s = sample standard deviation = 1.9 calls
n = sample size = 40
So, test statistics =
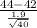 ~
~
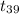
= 6.657
So, at 0.01 level of significance, the t table gives critical value of 2.426 for one-tailed test. Since our test statistics is way more than the critical value of t so we have sufficient evidence to reject null hypothesis as it will fall in the rejection region to the right of critical value of t.
Therefore, we conclude that the number of calls per salesperson per week is more than 42.