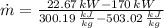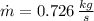Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The process made by the compressor at steady-state is modelled after the First Principle of Thermodynamics:
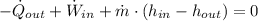
The mass flow rate is:
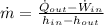
For ideal gases, specific enthalpies depends on temperature only. Properties at inlet and outlet are, respectively:
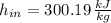
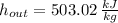
The mass flow rate of air is: