Answer:
a) 0.45 [kJ/kg*°C] iron and 4.22 [kJ/kg*°C] for water
b) 15.49 [C]
Step-by-step explanation:
This is a problem that applies principles of heat transfer with thermodynamics, to solve it we establish the following equality:
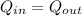
This is the heat that comes in is equal to the heat that comes out. We will take the heat that enters into the water like that released by the iron bar into the water.
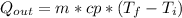
where:
m = mass of the bar = 100 [g] = 0.1 [kg]
cp = specific heat = 0.45 [kJ/kg*°C]
T_f = final temperature
Ti = initial temperature = 100 [°C]
a) Cp = 0.45 [kJ/kg*°C] (iron)
Cp = 4.22 [kJ/kg*°C] (water)
b)
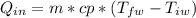
where:
m = mass of the water= 200 [g] = 0.2 [kg]
cp = specific heat = 4.22 [kJ/kg*°C]
T_f = final temperature
Tiw = initial temperature = 20 [°C]
We equate both equations and clear the final temperature.
![0.1*0.45*(T_(f)-100)=0.2*4.22*(T_(f)-20)\\0.045*T_(f)-4.5=0.844*T_(f)-16.88\\0.799*T=12.38\\T=15.49[C]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/middle-school/bzv78kbsznx9q4iy9futl66njpcwpyo13t.png)