Answer:
The ratio of heat transfer rate is 0.88
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
Case1 :
height of vertical surface, L = 1 m
width of vertical surface, w = 0.6 m
Case 2:
height of vertical surface, L = 0.6 m
width of vertical surface, w = 1 m
At an assumed film temperature of air = 300 K
then, read off from heat transfer table, temperature inverse β, surface area flow rate v, and Pr, to determine Rayleigh number for the two cases.
β = 1/300 = 0.00333 K⁻¹
v = 15.89 x 10⁻⁶ m²/s
Pr = 0.69
Case 1, L = 1 m
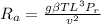
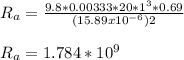
Case 2, L = 0.6 m
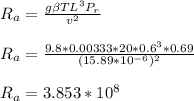
From the values of Rayleigh numbers above, case 1 is Turbulent flow while case 2 is laminar flow
Thus: C₁ = 0.1, n₁ = ¹/₃
C₂ = 0.59, n₂ = 1/4
Ratio of heat transfer rate is given as:
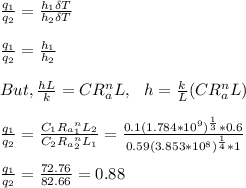
Therefore, the ratio of heat transfer rate is 0.88