Answer:
![[CFCl_3(g)]=(k_(-1))/(k_1)\cdot[CFCl_2(g)]\cdot [Cl(g)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g1xculnk0t1ovya8gztxz1tph898jve4ir.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
The equilibrium constant is equal to the ratio of the rate constant of the forward reaction to the rate constant of the reverse reaction:
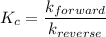
Then, using k₁ and k₋₁ for the rate constants of the forward and the reverse reactions, respectively:
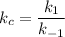
The equilibrium equation is:
CFCl₃(g) ⇄ CFCl₂(g) + Cl(g)
For which the equilibrium constant is:
![k_c=([CFCl_2(g)]\cdot [Cl(g)])/([CFCl_3(g)])=(k_1)/(k_(-1))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/jlz32rntefg6wubff98eh6mnjpbgw1kdc4.png)
Now you can write the equilibrium concentraion of CFCl₃(g) in terms of k₁, k₋₁, [CFCl₂(g)], and [Cl(g)]:
![[CFCl_3(g)]=(k_(-1))/(k_1)\cdot[CFCl_2(g)]\cdot [Cl(g)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g1xculnk0t1ovya8gztxz1tph898jve4ir.png)