Answer:
The new pressure of a gas is
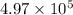 Pa
Pa
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Initial pressure
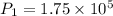 Pa
Pa
Initial temperature
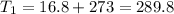 K
K
Final temperature
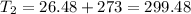 K
K
Initial volume
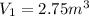
Final volume
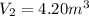
From ideal gas equation,
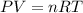
Where
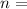 number of moles, here
number of moles, here
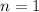 ,
,
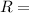 gas constant
gas constant
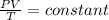
For finding new pressure of gas,
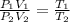
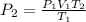
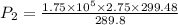
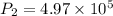 Pa
Pa
Therefore, the new pressure of a gas is
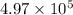 Pa
Pa