To solve this problem we will apply trigonometric and optical concepts that allow us to obtain the minimum distance required. The resolution of the eye is given under the following condition,
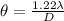
Here,
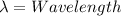
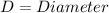
With the values we have that the diameter will be,
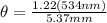
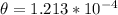
The relation between the distance of the lights and the distance from the eye to the lamp is given under the function,
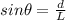
For small angles
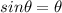 , then
, then
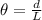
Here,
d = Distance between lights
L = Distance from eye to lamp
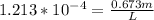
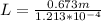
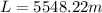
Therefore the distance will be 5.5km