To solve this problem we will apply the concepts related to resistance as a function of temperature, product of the relationship between the squared voltage and the power. Mathematically this is,
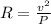
Here,
R = Resistance (At function of temperature)
v = Voltage
P = Power
Then we have,
R at 140°C (7 times room temperature),
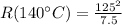
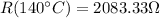
The relationship between normal temperature and increased temperature would then be given by,
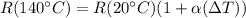
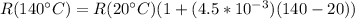
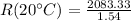
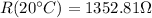
Therefore the correct value of the group of answer is 1350