Answer:
0.15g
Step-by-step explanation:
Given parameters:
Mass of ethanol = 1.37 x 10⁻¹g = 0.137g
Unknown:
Mass of acetic acid produced = ?
Solution:
The reaction equation is given by;
16H⁺ + 2Cr₂O₇²⁻ + 3CH₃CH₂OH → 3CH₃COOH + 4Cr³⁺ + 11H₂O
The equation above is balanced.
Now we solve from the known to the unknown i.e from the mass of ethanol to that of acetic acid.
First find the number of moles of ethanol;
number of moles =
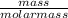
molar mass of CH₃CH₂OH = 12 + 3(1) + 12 + 2(1) + 16 + 1 = 56g/mol
number of moles =
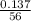 = 0.0025moles
= 0.0025moles
From the balanced reaction equation;
3 mole of CH₃CH₂OH produces 3 moles of CH₃COOH
0.0025mole of CH₃CH₂OH will produce 0.0025mole of CH₃COOH
Mass of CH₃COOH = number of moles x molar mass
molar mass of CH₃COOH = 12 + 3(1) + 12 + 2(16) + 1 = 60g/mol
Mass = 0.0025 x 60 = 0.15g