Answer:
Explanation:
(2)
Incidence Rate / 1000 =
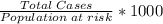
Incidence Rate / 1000 =
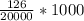
Incidence Rate / 1000 = 6.3
(3)
As there are 9,200 males in the population of 20,000, the number of females are (20,000-9,200) 10,800. Similarly, as there are 67 male cases from a total of 126, therefore, (126-67) 59 are female cases.
Male Incidence Rate / 10,000 =
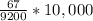
Male Incidence Rate / 10,000 =
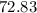
Female Incidence Rate / 10,000 =
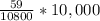
Female Incidence Rate / 10,000 =
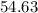
(b)
For proposal distribution we will simply use the incidence rates as the minimum threshold for each sexes as their acceptance rates to be regarded as affected (by the disease).
(c)
Male to Female Ratio =
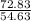
Male to Female Ratio = 1.333