Answer:
The kinetic energy must the electrons have in order to resolve a protein molecule is E = 4.36 ×
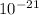 J
J
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data
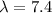 ×
×
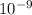 m
m
Mass of electron = 9.1 ×
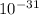 kg
kg
From de-broglie theory
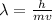
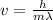
Put all the values in above formula we get
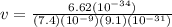
v = 0.98 ×
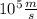
Kinetic energy is given by
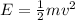
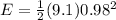 ×
×
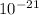 J
J
E = 4.36 ×
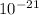 J
J
Therefore the kinetic energy must the electrons have in order to resolve a protein molecule is E = 4.36 ×
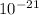 J
J