Answer:
Explanation:
Hello!
The variable of interest is:
X: Number of adults that said it is morally wrong to not report all income on tax returns of a sample of 745.
The researcher claim is that the population proportion of adults that consider it is morally wrong to not report all income on tax returns is 75%, symbolically p=0.75
Considering that the = symbol is always in the null hypothesis, then the statistical hypotheses are:
H₀: p=0.75
H₁:p≠0.75
α:0.01
Applying the Central Limit Theorem, you can approximate the distribution of the sample proportion to normal p'≈N(p;
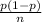 ) and thanks to this use the standard normal distribution to study the population proportion:
) and thanks to this use the standard normal distribution to study the population proportion:
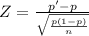 ≈N(0;1)
≈N(0;1)
The sample proportion is p'= 589/745= 0.79
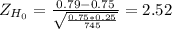
This test is a two-tailed test and the p-value is also two-tailed.
The p-value has two tails:
P(Z≤-2.52)= 0.00587
P(Z≥2.25)= 1 - P(Z≤2.52)= 1- 0.99413 = 0.00587
It is p-value= 2*0.00587= 0.01174
The decision rule for the p-value approach is
If p-value > α, you do not reject the null hypothesis
If p-value ≤ α, you reject the null hypothesis
The calculated p-value 0.01174 is greater than the significance level, the decision is to not reject the null hypothesis.
At a level of 1%, there is no significant evidence to reject the null hypothesis. Then you can conclude that the researchers claim is correct and the population proportion of adults that consider it is morally wrong to not report all income on tax returns is 75%.
I hope this helps!