Answer:
The speed of the skater is not depended on the mass of the skater.
Step-by-step explanation:
A skater is moving in a U shaped ramp with some mass m and velocity v.
We are basically required to find out the relationship between speed of the skater and mass of the skater.
When the mass of the skater is small:
As you can notice in the attached diagram 1, the skater is placed at the top of the ramp with some height h from the horizontal ground. The speed of the skater at this point is zero.
We know that the energy due to the position of a body is potential energy therefore, the skater has maximum potential energy at this point given by
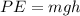
As you can notice in the attached diagram 2, the skater is in motion now and it has maximum speed at the lowest point on the ramp.
The potential energy is being converted into kinetic energy therefore, the skater has maximum kinetic energy at this point given by
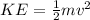
When the mass of the skater is large:
As you can notice in the attached diagram 3, the skater is placed at the top of the ramp now with a larger mass. The speed of the skater at this point is zero.
The potential energy of the skater is now increased due to the increase in the mass since the mass and PE are directly proportional.
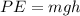
As you can notice in the attached diagram 4, the skater is in motion and it has maximum speed at the lowest point on the ramp.
The potential energy is being converted into kinetic energy and similarly skater has now greater kinetic energy due to increase in the mass.
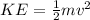
Notice that the total energy remains constant due to the principle of conservation of energy.
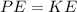
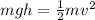
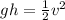
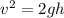
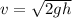
As you can notice, the speed of the skater is not depended on the mass of the skater rather it depends on the gravitational acceleration and height of the ramp which are constant in the case therefore, skater with small mass and larger mass both will have the same speed.
On the other hand, the total energy of the skater would be greater in the case of larger mass and lesser in the case of smaller mass.