Correct Question:
The closely packed cones in the fovea of the eye have a diameter of about 2 μm. For the eye to discern two images on the fovea as distinct, assume that the images must be separated by at least one cone that is not excited, by a distance of about 4 μm.If these images are of two point-like objects at the eye's 28-cm near point, how far apart are these barely resolvable objects? Assume the eye's diameter (cornea-to-fovea distance) is 2.0 cm.
Answer:
The objects are 0.000056 m apart
Step-by-step explanation:
From the diagram attached to this solution,
let the diameter of the eye = D = 2 cm 0.02 m
the distance between the objects = l
Position of the eye lens = E
the distance between objects and the lens of the eye = 28 cm = 0.28 m
The images are separated by a distance of 4 μm = 4 * 10⁻⁶m
Observing the attached diagram properly, ΔABE and ΔECD are similar
Therefore,
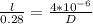
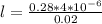
l = 0.000056 m